2024. 10. 28. 13:38ㆍ[5분 SOTA 논문 컨트리뷰션 리뷰]
본 포스팅에서는 ESCAPE: Encoding Super-keypoints for Category-Agnostic Pose Estimation (CVPR 2024) 논문을 간단히 리뷰하였습니다.
그림과 설명은 논문자료를 참고하였습니다.
원문 링크:
CVPR 2024 Open Access Repository
ESCAPE: Encoding Super-keypoints for Category-Agnostic Pose Estimation Khoi Duc Nguyen, Chen Li, Gim Hee Lee; Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024, pp. 23491-23500 Abstract In this paper we tackle t
openaccess.thecvf.com
1. Motivation
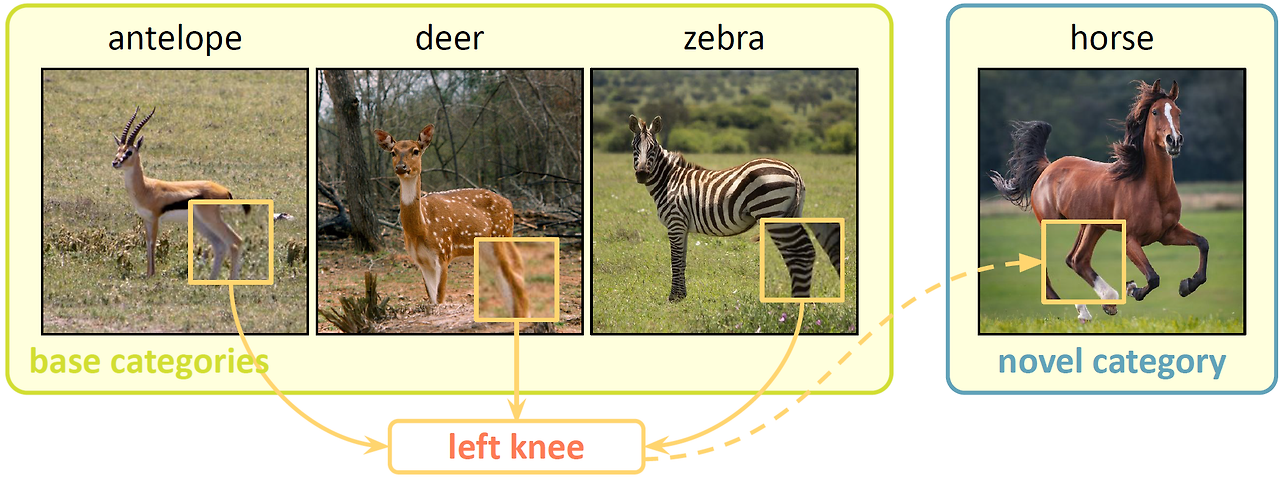
기존 연구들은 support 그리고 query samples의 feature 간의 loacl matching에 의존하거나 support keypoint identifiirer를 필요로 한다.
하지만, local matching는 sparse samples에 sensitivity 하며 overfitting에 취약하다.
support keypoint identifirer는 real-world의 특성 때문에 비현실적이다.
본 논문에서는 이러한 한계를 극복하기 위해 ESCAPE - a Bayesian framework를 제안한다.
ESCAPE는 keypoint feature에 대한 사전 지식을 학습하고, 서로 다른 범주에서 의미적으로 관련된 super-keypoints를 통해 이를 새로운 범주에 적용하는 방식이다.
2. Unique methodology
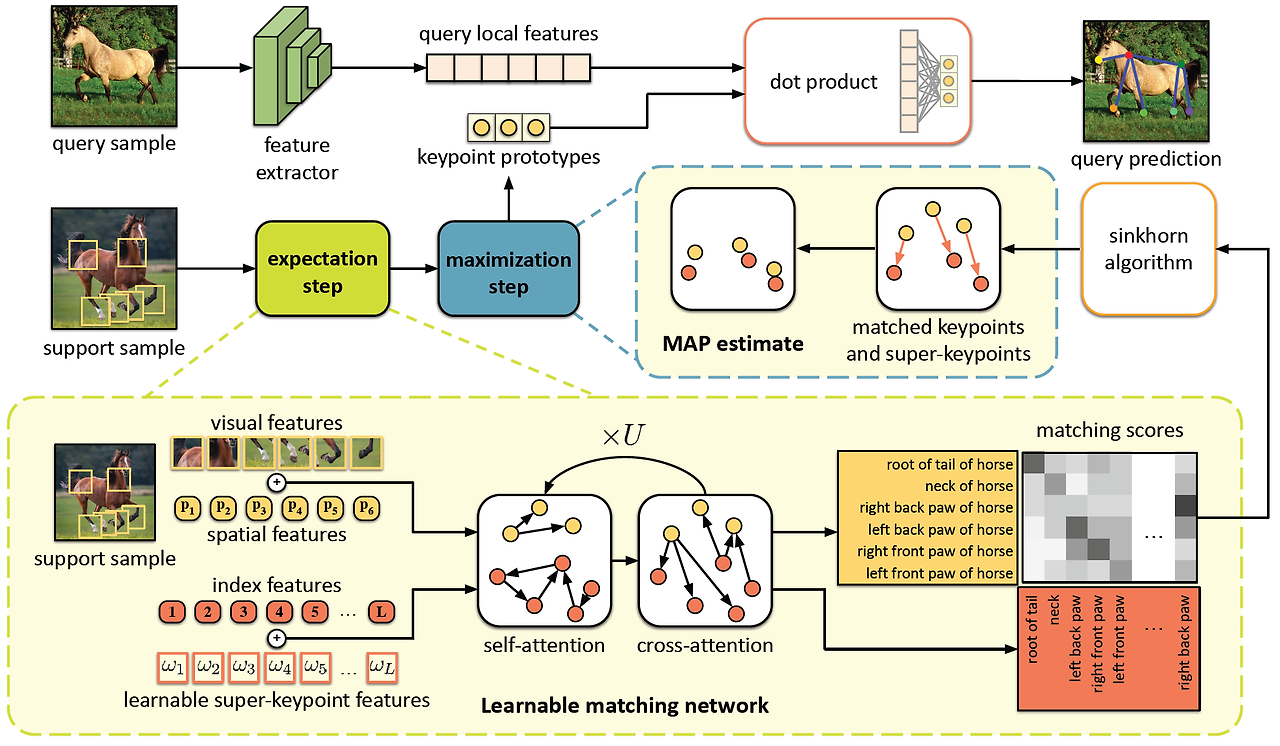
본 논문에서 제안한 방법은 EM(Expectation-Maximization) 알고리즘을 활용하여 keypoint prototype을 확률적으로 optimize 한다.
해당 과정에서 support samples과 학습된 super-keypoints를 모두 고려한다.
- Expectation Step (E-Step): 새로운 키포인트를 다양한 슈퍼 키포인트와 정렬한다. 이 과정은 학습 가능한 matching network를 통해 이루어진다.
- Maximization Step (M-Step): matching 된 super-keypoint에 인코딩 된 통계 정보를 keypoint prototype으로 직접 전이한다.
3. Results
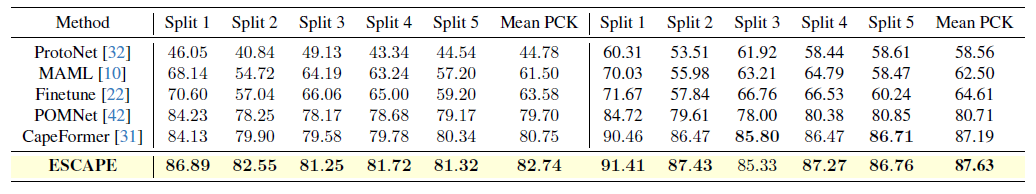
Table 1은 MP-100 dataset에 대한 정량적 실험 결과이다.
해당 실험결과 본 논문에서 제안한방법인 ESCAPE가 기존 SOTA방법과 비교하였을 때 1-shot setting에서 약 2.5%, 5-shot setting에서는 약 0.5% 더 높은 성능을 보여주고 있다.

Figure 6.은 squirrel, woodpecker의 matching결과를 보여준다.
그림의 왼쪽은 squirrel, woodpecker의 support 이미지가 표시되며, 오른쪽은 Simple matching, Learnable matching network를 통해 align 된 super-keypoint이다.
실험 결과 Simple matching은 squirrel의 8번, woodpecker의 4번 결과와 같이 SUV 또는 short sleeved outwear와 같은 관련 없는 super-keypoint를 align한다.
반면, Learnable matching network 왼쪽에 나와있는 point와 유사한 개념에 맞게 align한다.